Modern Computer Architecture and Organization
Modern Computer Architecture and Organization, by Jim Ledin. Published by Packt Publishing.
Chapter 6, Exercise 1
Rate monotonic scheduling (RMS) is an algorithm for assigning thread priorities in preemptive, hard real-time applications in which threads execute periodically. RMS assigns the highest priority to the thread with the shortest execution period, the next highest priority to the thread with the next shortest execution period, and so on. An RMS system is schedulable, meaning all tasks are guaranteed to meet their deadlines (assuming no inter-thread interactions or other activities such as interrupts cause processing delays) if the following condition is met:
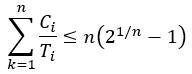
This formula represents the maximum fraction of available processing time that can be consumed by n threads. In this formula, Ci is the maximum execution time required for thread i, and Ti is the execution period of thread i.
Is the following system composed of three threads schedulable?
| Thread | Execution time (Ci), ms | Execution period (Ti), ms |
|---|---|---|
| Thread 1 | 50 | 100 |
| Thread 2 | 100 | 500 |
| Thread 3 | 120 | 1000 |
Answer
First, evaluate the left side of the RMS formula using the data from the table:
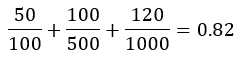
Then evaluate the right side of the RMS formula:
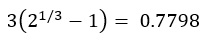
Because 0.82 is not less than or equal to 0.7798, this set of tasks is not schedulable in RMS.